# Server management
# Automatic restarting after shutdown
So you probably want to restart your server in a timed interval. Shutting it down is easy, bringing it back up is the hard part.
# Linux
If you've followed the installation guide in these docs, you will have 7 Days to Die running with LGSM which comes with some very handy management scripts. See their docs (opens new window) for a detailed explanation.
However, you may have installed 7 Days to Die in a different way. Fear not, there's options for you aswell!
# Systemd
systemd (opens new window) in installed on many distros these days. We will use it to turn your server into a service which will automatically handle things like log management, service monitoring, ... for you. Systemd can do a lot of things for you and is very customizable, we recommend you read up on it for more info but here is a basic example service file to get you started.
[Unit]
Description=7 Days to Die
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=sdtd
WorkingDirectory=/home/sdtd
ExecStart=/home/sdtd/startserver.sh -configfile=serverconfig.xml
Restart=on-failure # or always, on-abort, etc
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
# Script cronjob
This approach is basic but it gets the job done.
#!/bin/sh
SERVICE='7DaysToDieServer'
if ps ef | grep -v grep | grep $SERVICE > /dev/null
then
echo "$SERVICE service running, everything is fine"
else
echo "$SERVICE is not running"
nohup /home/sdtd/7d2d/startserver.sh -configfile=serverconfig.xml &
fi
Credit to Highhope for this script
# Windows
# Batch script
- Create a batch file. For example: startdedicated.bat
- Make sure the 7DTD Server is not already running, if so shut it down using the shutdown command via Telnet so that you have a clean saved state
- Run the batch file (make sure you are Admin or have the right permissions)
- DO NOT CLOSE the batch file.
- Every time you shutdown the server using Telnet/RCON and the shutdown command, the batch file will restart the server and you will see a "restarting" time stamp in the console/command window.
@echo off
title startdedicated.bat
set LOGTIMESTAMP=
IF EXIST 7DaysToDieServer.exe (
set GAMENAME=7DaysToDieServer
set LOGNAME=output_log_dedi
) ELSE (
set GAMENAME=7DaysToDie
set LOGNAME=output_log
)
:: --------------------------------------------
:: REMOVE OLD LOGS (only keep latest 20)
for /f "tokens=* skip=19" %%F in ('dir %GAMENAME%_Data\%LOGNAME%*.txt /o-d /tc /b') do del %GAMENAME%_Data\%%F
:: --------------------------------------------
:: BUILDING TIMESTAMP FOR LOGFILE
:: Check WMIC is available
WMIC.EXE Alias /? >NUL 2>&1 || GOTO s_start
:: Use WMIC to retrieve date and time
FOR /F "skip=1 tokens=1-6" %%G IN ('WMIC Path Win32_LocalTime Get Day^,Hour^,Minute^,Month^,Second^,Year /Format:table') DO (
IF "%%~L"=="" goto s_done
Set _yyyy=%%L
Set _mm=00%%J
Set _dd=00%%G
Set _hour=00%%H
Set _minute=00%%I
Set _second=00%%K
)
:s_done
:: Pad digits with leading zeros
Set _mm=%_mm:~-2%
Set _dd=%_dd:~-2%
Set _hour=%_hour:~-2%
Set _minute=%_minute:~-2%
Set _second=%_second:~-2%
Set LOGTIMESTAMP=__%_yyyy%-%_mm%-%_dd%__%_hour%-%_minute%-%_second%
:s_start
:: --------------------------------------------
:: STARTING SERVER
echo|set /p="251570" > steam_appid.txt
set SteamAppId=251570
set SteamGameId=251570
set LOGFILE=%~dp0\%GAMENAME%_Data\%LOGNAME%%LOGTIMESTAMP%.txt
echo Writing log file to: %LOGFILE%
7DaysToDieServer.exe -logfile "%LOGFILE%" -quit -batchmode -nographics -configfile=serverconfig.xml -dedicated
echo.
for /F "tokens=2" %%i in ('date /t') do set mydate=%%i
set mytime=%time%
echo Restarting Server: %mydate%:%mytime%
echo.
goto start
timeout 3
:start
startdedicated.bat
Credit to sLim Long#9007
# Service
FireDaemon (opens new window) is a tool that allows you to run any programs as a Windows service.
Now, we won’t go into how to install and setup a dedicated server. We assume you have already installed your dedicated server on windows, configured your serverconfig.xml with appropriate settings, and have your server in a directory located at c:\7d2d\
Install and launch FireDaemon. You’ll want to “add a new service”, to do this hover over the + symbol and you will get a tool-tip. Your setting will look something like this. The name doesn’t matter so long as if you’re using multiple servers or instances on this server, you’ll want them named differently.
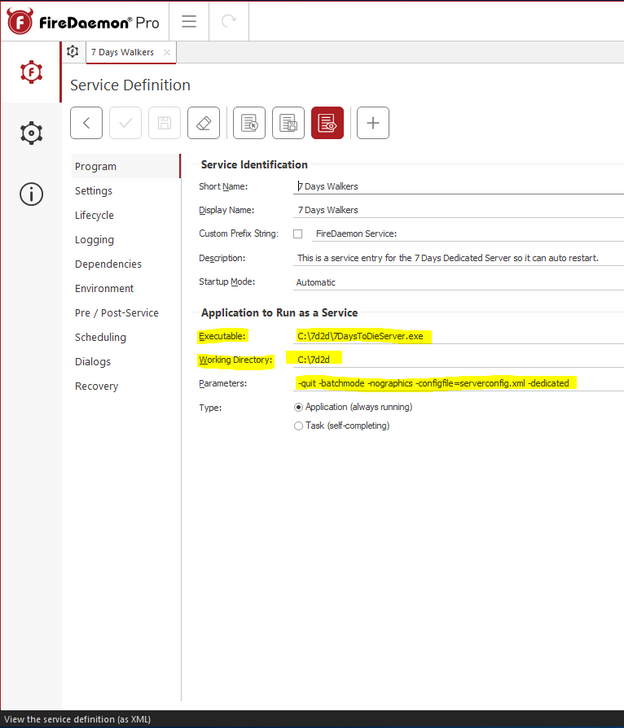
Settings:
- Executable = “The Path to the file you want to execute.” Since you’re going to use FireDaemon to babysit this application as a “process” you DON’T want to use the batch file. Point this directly at your server.exe.
- Working Directory = This is where that executable lives. It will auto-magically populate.
- Parameters = These are the settings after the executable that tell it what to do. In the case of a dedicated server they are:
-quit -batchmode -nographics -configfile=serverconfig.xml -dedicated
Now, on the left hand side you have some other options. Click on “Settings”
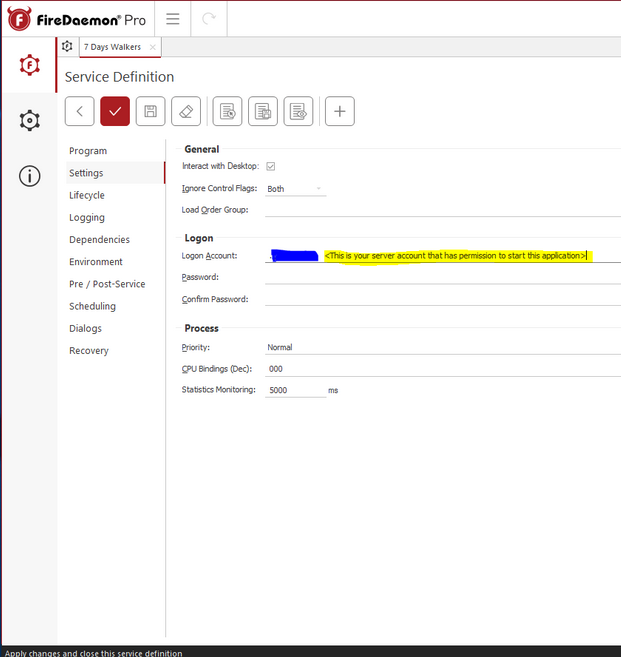
Logon: A user on windows needs permissions to launch an application. The same applies for services. FireDaemon isn’t a user, it’s a utility. So, FireDaemon needs to be told a user account it can use to execute the server application. You can use any user account that has permission to execute the app. Best practice dictates you create a special user account that has no other system privileges, but that’s beyond the scope of this guide. In the case below we are RDP’d into a Windows VPS. So we are just using the same user account and PW I use to manage my VPS over RDP.
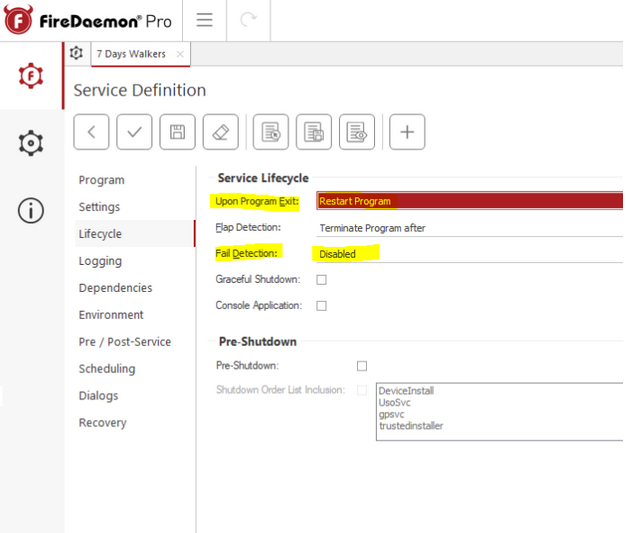
Now, click the left hand item “LifeCycle”. This is where we configure the magic. “Service Lifecycle”
- Upon Program Exit: Set this to “restart program”
- Fail Detection: Disable this feature. Our only failure detection will be whether the process is present in the process list in task manager, or not.
Leave the other options unchecked as in the screenshot. Now, click the disk icon, which is “Save”
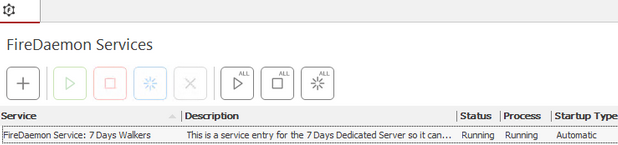
You now see your process running, and your server should have started.
WARNING
When you run the server from the batch file, you get a local window console you can interact with. That will NOT be the case with FireDaemon. The process will be running in the background. So, to console in you’ll either need to log in via the control panel, or you’ll need to telnet to your server. Make sure you accommodate for this in the serverconfig.xml because by default; control panel is disabled.
I assume if you’re trying to handle automatic restarts, then you are already using a management tool, or something else which would mean you likely have already done this configuration.
Credit to 2ndRecon